推断打印结果
1 | public static void main(String args[]) { |
结果:1
2true
false
解析:由于b的值确定且被final修饰,会被当做编译期常量使用,即编译期出现b变量的地方会被直接替换,
替换后,a和c都指向字符串常量池中的hello2地址,故a==c为true;而String e = d + 2;会被编译器转换为类似于 String e = new StringBuilder(d).append(“2”); 故 a==e为false.
请画出a,b,c,d内存分布图
1 | public static void main(String args[]) { |
解析: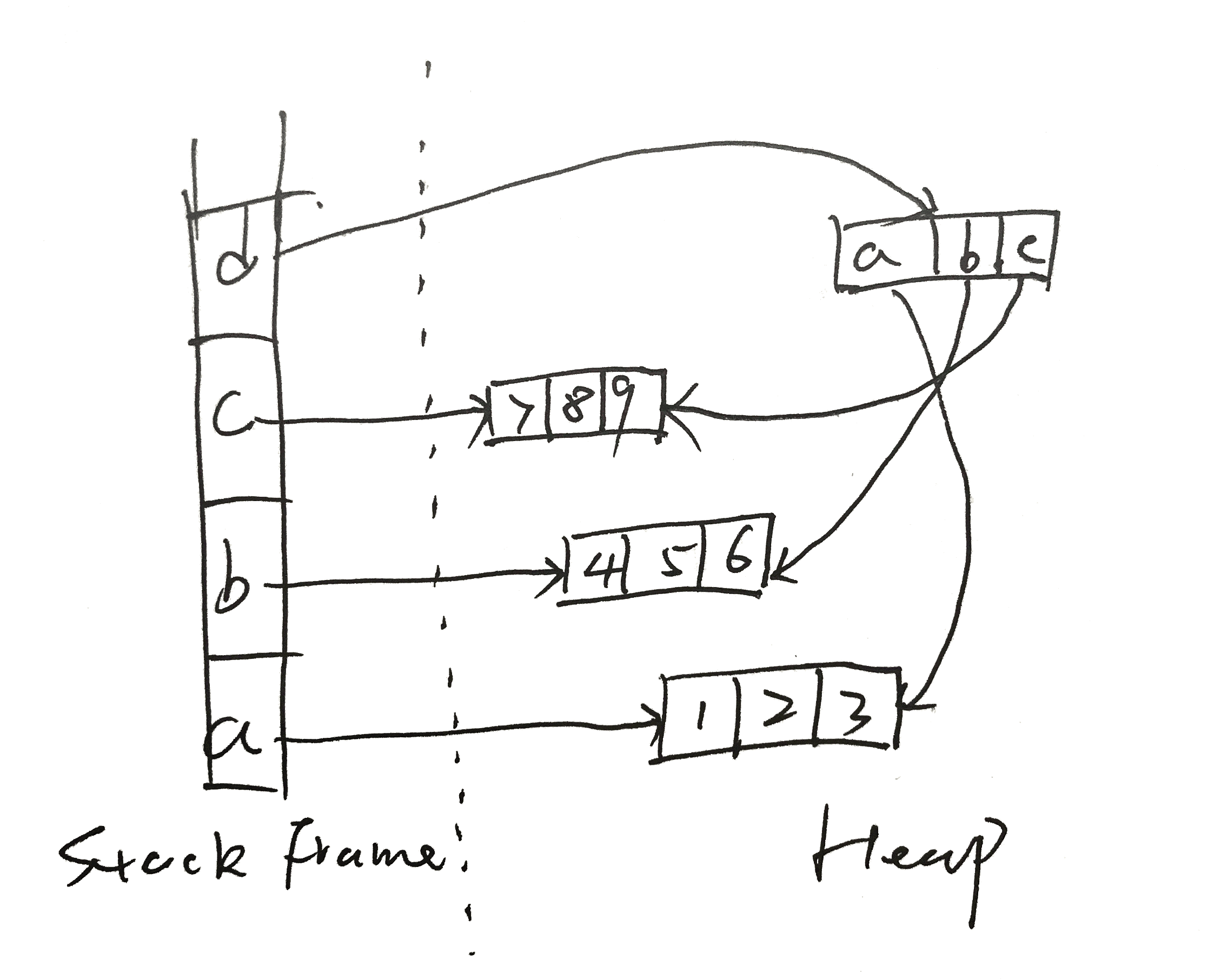
判断输出结果
I
1 | public class Example { |
运行结果:1
2Hello
ahc
解析: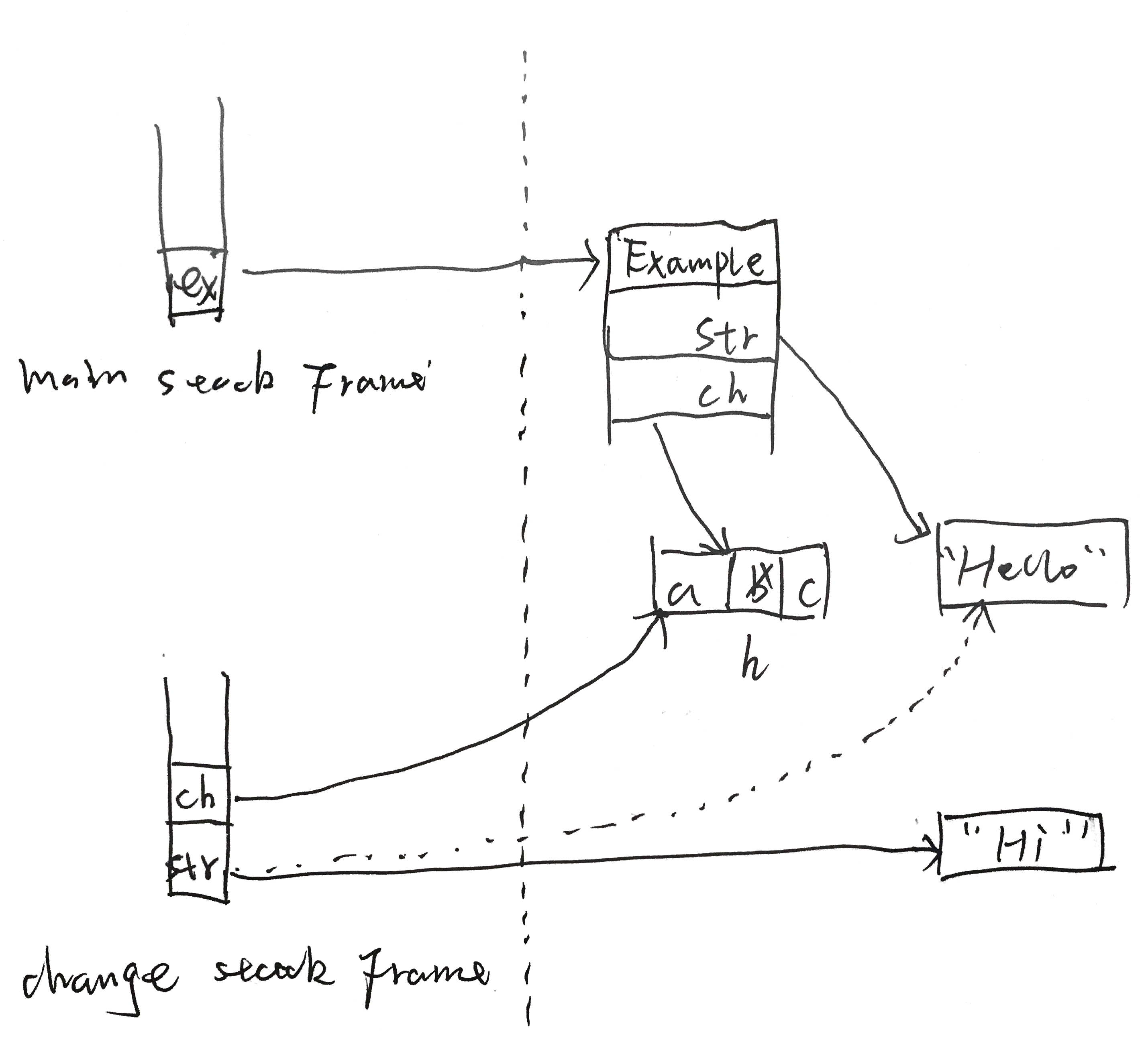
II
1 | public class Person { |
哪些操作是原子性操作
1 | x = 10; //语句1 |
1 | x = 10; |
解析:注意y = x,需要读取和赋值,并非原子性操作。
以下代码是否有问题,并解释。
1 | public class Example { |
解析:ouput和output2两个方法分别使用类对象和类实例对象的锁,两个线程不会竞争同一个锁资源,因而不会产生互斥,从而导致输出混乱。
SQL查询
员工表emp:
| empno | ename | job | mgr | hiredate | sal | comm | deptno |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7369 | SMITH | CLERK | 7902 | 1980-12-17 | 800.00 | NULL | 20 |
| 7499 | ALLEN | SALESMAN | 7698 | 1981-02-20 | 1600.00 | 300.00 | 30 |
| 7521 | WARD | SALESMAN | 7698 | 1981-02-22 | 1250.00 | 500.00 | 30 |
| 7566 | JONES | MANAGER | 7839 | 1981-04-02 | 2975.00 | NULL | 20 |
| 7654 | MARTIN | SALESMAN | 7698 | 1981-09-28 | 1250.00 | 1400.00 | 30 |
| 7698 | BLAKE | MANAGER | 7839 | 1981-05-01 | 2850.00 | NULL | 30 |
| 7782 | CLARK | MANAGER | 7839 | 1981-06-09 | 2450.00 | NULL | 10 |
| 7788 | SCOTT | ANALYST | 7566 | 1987-07-13 | 3000.00 | NULL | 20 |
| 7839 | KING | PRESIDENT | NULL | 1981-11-17 | 5000.00 | NULL | 10 |
| 7844 | TURNER | SALESMAN | 7698 | 1981-09-08 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 30 |
| 7876 | ADAMS | CLERK | 7788 | 1987-07-13 | 1100.00 | NULL | 20 |
| 7900 | JAMES | CLERK | 7698 | 1981-12-03 | 950.00 | NULL | 30 |
| 7902 | FORD | ANALYST | 7566 | 1981-12-03 | 3000.00 | NULL | 20 |
| 7934 | MILLER | CLERK | 7782 | 1982-01-23 | 1300.00 | NULL | 10 |
部门表dept:
| deptno | dname | loc |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | ACCOUNTING | NEW YORK |
| 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 40 | OPERATIONS | BOSTON |
查询部门表在员工表中不存在的部门号;
1 | SELECT d.deptno |
查询工资高于部门平均工资的员工;
1 | SELECT e2.ename,e2.sal,e2.deptno,r1._avg |
查询部门工资前三名的员工;
1 | SELECT t0.deptno, t0.ename, t0.sal |
解析: 员工工资排名前3,可以转换为: 工资大于等于自己的人数(count)小于等于3
